
China exhibited the most rapid increase in the number of publications (from 0 in 2000 to 69 in 2021). The journals, authors, and institutions that published the most relevant literature came from these three countries. The top three countries with the highest number of publications were China, the USA, and Japan. PM has become a fascinating topic (with relative research interest ranging from 0.0018% in 2000 to 0.0044% in 2021) and a global public health issue. Results: A total of 1,435 publications were retrieved. Methods: A bibliometric analysis was performed to evaluate global production and development trends in PM since 2000 and the keywords associated with PM. This study aimed to analyze PM research trends by reporting on publication trends since 2000 and identifying influential journals, countries, authors, and keywords involved in PM. 3Department of Anaesthesiology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, Chinaīackground and purpose: Pathologic myopia (PM) is an international public health issue.2Key Laboratory of Ocular Fundus Diseases, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China.1Department of Ophthalmology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China.LASIK is not recommended for patients with degenerative myopia.Jingyuan Yang 1,2 †, Shan Wu 3 †, Chenxi Zhang 1,2, Weihong Yu 1,2, Rongping Dai 1,2 and Youxin Chen 1,2 *.Rigid gas permeable lenses offer good optics and physiological health (a minus lenticular design may be appropriate to minimize complications and discomfort of edge thickness) Soft contact lens offer comfort and convenience, but closely monitor for hypoxia if not using silicone-hydrogel lenses. Patient’s refractive error can be corrected with contacts (soft and rigid gas permeable lenses).
Recommend polycarbonate for greater protection, plastic (zylonite) frames to mask increased edge thickness of lens with special edge polishing and buffing to improve lens cosmetics.

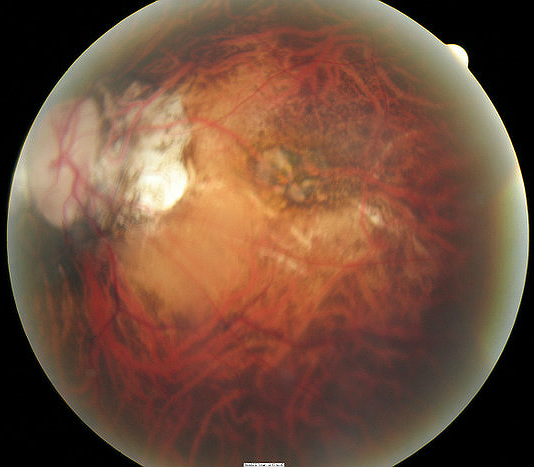
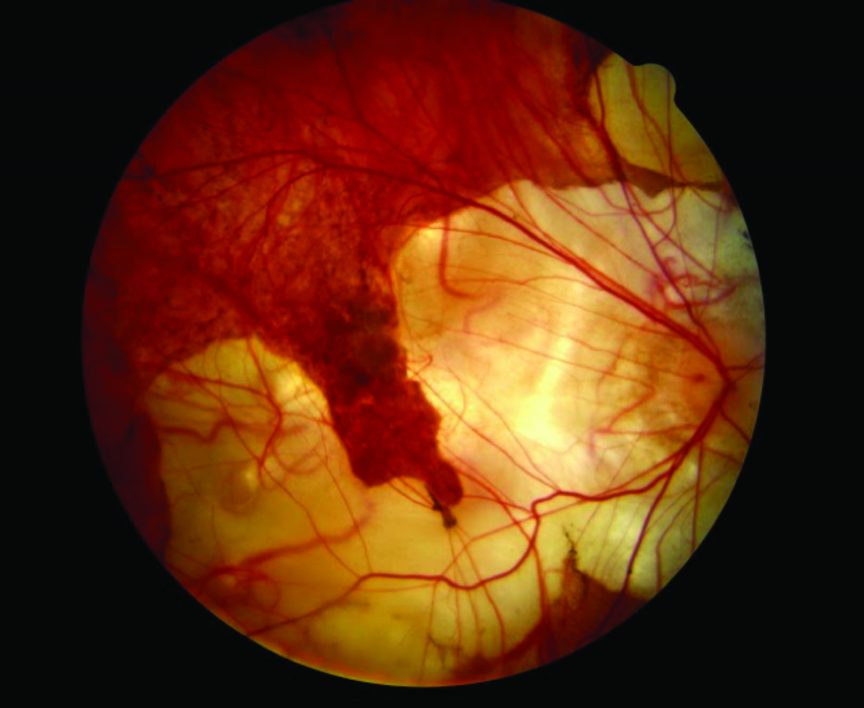
Subretinal neovascular membrane with overlying retinal pigment epithelial hyperplasia (Fuchs’ spot).Lacquer cracks or breaks in Bruch’s membrane with accompanying choroidal atrophy.Patchy choroidal atrophy within the posterior pole.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
